Introduction
In today’s complex financial landscape, managing public funds effectively is essential to ensuring both economic stability and the provision of quality public services. The role of public financial management (PFM) has evolved significantly in response to globalization, economic challenges, and increasing demands for transparency. At the heart of these financial systems lies the Institute of Government Accounts and Finance (IGAF), an organization dedicated to improving the accountability, efficiency, and integrity of public finance across governments worldwide.
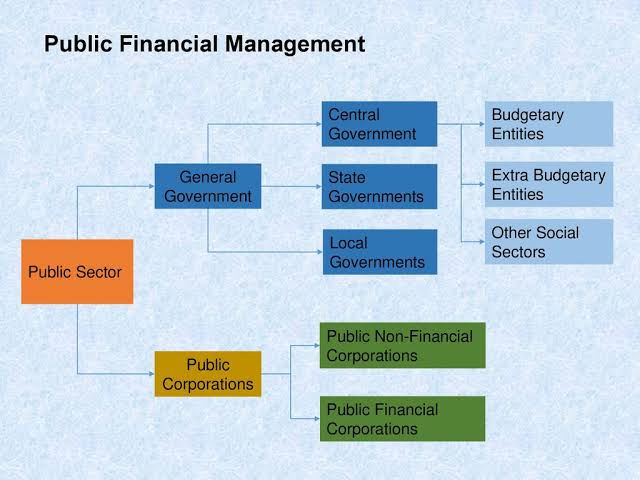
Public financial management encompasses a broad range of activities, including budgeting, accounting, auditing, and the overall management of public resources. IGAF’s role in this process is pivotal, providing the training, expertise, and frameworks necessary to ensure that governments handle financial resources responsibly and transparently. This blog will explore the significance of IGAF in public financial management, its core functions, and its long-term impact on government financial practices.
What is the Institute of Government Accounts and Finance (IGAF)?
The Institute of Government Accounts and Finance (IGAF) is a professional body focused on advancing the practice of financial management within government entities. Established to promote accountability, transparency, and efficiency in the public sector, IGAF provides government employees, accountants, auditors, and financial managers with the knowledge, tools, and resources to enhance their expertise.
The institute’s mission is to establish a robust framework for public financial management that ensures governments allocate and spend public resources responsibly. IGAF’s role is instrumental in shaping the systems, policies, and practices that guide how governments manage their financial affairs, ensuring these practices are not only effective but also aligned with international standards and best practices.
Through various initiatives like professional training, development of financial management standards, research, and policy advocacy, IGAF seeks to foster a more transparent, accountable, and efficient public sector. Its activities span across government entities, aiming to improve the way public finances are managed from local to national levels.
The Importance of Public Financial Management (PFM)
Effective public financial management is the cornerstone of good governance. It directly influences the efficiency of government services, economic stability, and the level of trust between the government and its citizens. Poor financial management can lead to inefficiencies, budget overruns, corruption, and the misallocation of resources, ultimately undermining public trust.
Key Components of Public Financial Management:
Budgeting and Financial Planning: At the core of PFM is the development of an annual budget that determines how public resources are allocated across various sectors, including healthcare, education, infrastructure, defense, and social welfare. Proper budgeting is critical to ensuring resources are used in ways that meet public needs while maintaining fiscal discipline.
Accounting and Reporting: Governments must maintain accurate records of their financial transactions to ensure transparency and accountability. This includes adhering to standardized accounting systems that allow for the proper tracking of government spending and revenue.
Auditing and Oversight: Auditing is essential to verify that government funds are being spent appropriately and that public institutions are adhering to legal and financial regulations. Auditors assess whether government departments and agencies are managing their financial resources effectively, while also identifying areas for improvement.
Public Debt Management: Governments must also manage their debt levels responsibly, ensuring they can meet obligations without jeopardizing the financial stability of the state or the economy.
By improving these key areas, IGAF contributes significantly to the broader goal of enhancing governance and economic performance in the public sector. This ensures that public resources are allocated efficiently, and governments remain accountable for their financial decisions.
Core Functions of IGAF
IGAF serves as a multifaceted institution, playing several critical roles in enhancing the management of public finances. Below are the key functions of IGAF, each of which contributes to strengthening financial management in the public sector:
1. Training and Capacity Building
A fundamental component of IGAF’s work is providing continuous education and training to professionals in public finance. Through a range of specialized programs, workshops, and certifications, IGAF equips public sector employees with the skills they need to manage finances effectively. This training covers various aspects of public financial management, including government accounting, auditing, budgeting, financial reporting, and public procurement.
By providing access to this knowledge, IGAF ensures that government officials stay up-to-date with the latest developments in financial regulations, accounting standards, and management techniques. This constant skill development fosters a highly competent public finance workforce, capable of handling the complexities of modern financial systems.
2. Development of Standards for Financial Management
One of IGAF’s most important roles is to develop and promote standardized accounting, auditing, and financial management practices across government entities. Through collaboration with international bodies such as the International Public Sector Accounting Standards Board (IPSASB), IGAF ensures that governments adhere to recognized standards for financial reporting and budgeting.
These standards help ensure consistency and transparency in the financial management processes of governments worldwide, making it easier to compare financial statements, track spending, and evaluate performance. Adopting these standards also helps governments align with global best practices, strengthening their credibility on the international stage.
3. Policy Advocacy and Research
IGAF also contributes to the development of public financial management policies and frameworks. By conducting research on emerging trends and challenges in PFM, IGAF generates valuable insights that can guide government policy and decision-making.
Moreover, IGAF works closely with policymakers to influence the adoption of financial management reforms that promote efficiency, accountability, and transparency. These policy reforms may involve changes to budgeting processes, financial reporting requirements, or the creation of new regulations aimed at improving public sector financial performance.
4. Promoting Good Governance and Financial Accountability
IGAF’s efforts are critical to improving governance and ensuring financial accountability. By providing governments with the tools and expertise needed to manage finances effectively, IGAF helps reduce the risk of corruption, wasteful spending, and inefficiency. Transparent financial practices also enable citizens to hold their governments accountable, fostering greater trust in public institutions.
IGAF and Budgeting: Ensuring Effective Resource Allocation
Budgeting is one of the most important functions of government finance. The government budget determines how national resources are allocated to various sectors and services. It is a tool for setting priorities and ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
IGAF plays a key role in ensuring that budgeting processes are transparent, inclusive, and aligned with broader economic goals. Through its training programs and policy guidelines, IGAF ensures that governments at all levels follow sound budgeting principles. These principles include:
Evidence-Based Budgeting: Budget decisions should be grounded in data and research to ensure that resources are allocated where they will have the most significant impact on public welfare.
Fiscal Responsibility: Governments must ensure that their spending is sustainable and does not lead to excessive debt accumulation.
Public Participation: Including citizens in the budgeting process ensures that the allocation of resources reflects the needs and priorities of the people.
Through its role in improving budgeting practices, IGAF helps governments make informed decisions about public spending, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and equitably.
The Role of IGAF in Auditing and Financial Reporting
Auditing and financial reporting are critical elements of good public financial management. IGAF contributes to the development of auditing standards that help ensure governments are held accountable for their financial decisions. Public sector auditors are responsible for reviewing financial statements and ensuring that funds are being used appropriately.
There are two main types of audits that IGAF focuses on:
- Internal Audits: Internal auditors examine a government’s financial and operational processes to identify weaknesses, inefficiencies, and potential fraud. They provide recommendations for improving financial controls and performance, ensuring that public resources are spent responsibly.
- External Audits: External auditors, typically independent professionals, review government financial statements to verify their accuracy and ensure compliance with legal requirements. External audits help ensure the credibility and reliability of financial reporting.
By promoting rigorous auditing practices, IGAF helps strengthen transparency and accountability in the public sector, reducing the risk of financial mismanagement and fraud.
Challenges in Public Financial Management and the Role of IGAF
Despite the significant strides made in public financial management, many governments face persistent challenges. Political interference, corruption, lack of capacity, and weak institutions can undermine financial management systems. IGAF’s work is critical in addressing these challenges and promoting reforms that enhance the efficiency and transparency of public financial systems.
- Political Interference: In some cases, government financial systems may be subject to political pressures that affect budgeting decisions or the allocation of resources. IGAF works to promote impartial financial management practices and ensures that budgets are formulated based on national priorities rather than political interests.
- Capacity Building: Developing countries may face a shortage of skilled professionals capable of managing complex public finances. IGAF’s training programs help fill this gap by providing government employees with the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Corruption and Mismanagement: Public financial management systems can be vulnerable to corruption. By establishing strong auditing frameworks and promoting transparency, IGAF helps reduce the opportunities for corrupt practices.
The Future of IGAF and Public Financial Management
As global financial systems continue to evolve, IGAF’s role will become even more important. Emerging trends such as digitalization, the use of big data, and the integration of technology into financial management will require new approaches and adaptations. IGAF will continue to support governments in navigating these changes and ensuring that financial systems remain effective, transparent, and accountable.
IGAF’s continued collaboration with international bodies will further strengthen global public financial management practices, ensuring that governments around the world can face future challenges with confidence.
Conclusion
The Institute of Government Accounts and Finance (IGAF) is at the forefront of advancing public financial management. Through its training, research, policy advocacy, and development of financial standards, IGAF ensures that governments handle public funds responsibly and transparently. By playing a crucial role in strengthening accountability and efficiency in the public sector, IGAF contributes to the overall stability and prosperity of nations.
As public financial management systems evolve in response to new challenges and global changes, the continued work of IGAF will be essential in promoting good governance, financial transparency, and the responsible management of public resources. The institute’s efforts ensure that governments remain accountable to their citizens and that public funds are used to improve the well-being of society as a whole.